Compact Flash (CF) Cards and Handheld PCsCESD|200061Applies To
OverviewThis article provides an overview of Compact Flash storage cards and discusses the technical constraints of using CF cards with Windows CE based Handheld PCs. GuideCF Cards or Compact Flash cards are the original generation of storage solutions with a mobile footprint. OverviewCF Cards were an important step forward in mobile storage solutions. Unlike Hard drives they contain no mechanical parts and provide a constant, reliable non-volatile way of storing data without a power supply. Previous technologies used volatile memory technologies, requiring a constant power source to maintain data integrity. The Compact Flash specification defines a Solid State (No moving parts), non-volatile (doesn't require any external component to maintain the integrity of the stored information i.e. a power supply). CF Cards run at either 3.3 or 5 volts, requiring less than 5% of the power needed by a small hard disk drive that operates within the PCMCIA specification. One of the greatest features of CF cards is that they operate using the ATA / ATAPI specification as well as supporting the PCMCIA ATA specification. This means that CF Cards can operate using the same driver technology as Hard Disks and PCMCIA Storage solutions. Allowing CF cards to operate in a raft of devices, under a range of operating systems without the need for additional software. The life span of a CF card with its built in defect management and error correction technologies stored data given normal use is roughly 100 years with no data deterioration. CF Cards can withstand falls equivalent to that of a 10ft (3 metres) drop. Current day CF Cards range from sizes of 2MB up to specialist cards with 5,120MB (5GB) or more in capacity. CF Cards are a very cheap way to increase the storage capacity of your Handheld PC. CompatibilityThere are two versions of the Compact Flash Specification. The primary difference between the older type 1 specification and the newer type 2 is the data rate supported by the card. Type 1 cards support data transfer rates of 8MB/s where as Type 2 cards will support speeds of up to 16MB/s. The CF 2 specification is backward compatible with the type 1 specification but crucially Type 2 cards can be used with type one hardware at the slower transfer rate. Ensuring compatibility at least on the hardware level.
Whether a CF card is compatible with a particular device is down to the software which the device runs on. All digital media must conform to a File System specification. Examples of file systems are FAT, NTFS, Ext2, Ext3. The most common and widely supported File System is the Microsoft FAT or File Allocation Table method. FAT is supported by virtually all operating systems. Unfortunately there are several sub specifications of the FAT specification. This is where complication can arise with supporting different sized CF cards.
Using a CF Card between a Handheld PC and another PC can be complicated by Windows NT. If you wish to use your CF card in Windows NT (Windows NT 3.51, NT 4.0, 2000, XP, 2003) you should not attempt to format your card using Disk Administrator or Windows Explorer. Windows 2000, for example is able to support hard disk optimised File Systems running on the FAT specification beyond those supported by the original MS-DOS implementation. As a result of using more advanced cluster sizes Windows will automatically attempt to make the optimum use of your CF card. Handheld PC devices are only able to support the MS-DOS implementation of FAT. While MS-DOS can only support a maximum FAT12 volume of 8MB, Windows 2000 can technically support a FAT12 volume of 32MB. While Windows 2000 has been programmed to format 32MB cards using FAT16, cards of sizes between 8MB and 16MB may be formatted using FAT12, rendering it unreadable by Windows CE. The same may be true for CF Cards over 512MB which may be formatted to FAT32 by default. Cards over 2GB must be formatted to FAT32. By default Windows XP will format cards larger than 32MB as FAT32. As a result the following restrictions apply:
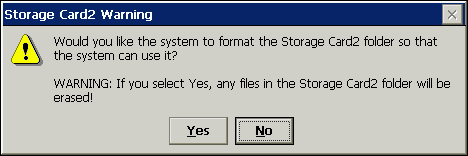
Formatting a CF CardWindows CE based Handheld PCs are able to format a CF card. However the Operating System has been limited to being able to format a card but only if it is unable to successfully read the volume. In such an event an image similar to the following will be displayed.
We recommend that you use MS-DOS or Windows 95 OSR2 / 98 / 98SE / Millennium to format the card in an external reader. Using DOS or Windows 9x will ensure that you maintain the correct File System standards.
You can use 2000, XP or 2003 to format the card however it may render the card unusable in Windows CE if not performed correctly. To format a CF Card using MS-DOS or the command prompt: At the command prompt type:
Where X: is the drive letter assigned to your CF reader. Follow the instructions on the screen. To format using Windows 95, 98, 98SE
To format using Windows 2000, XP, 2003
ConclusionCF Cards are the ideal way to expand the functionality of your Handheld PC by increasing it's memory. One feature of all Handheld PCs is the presence of at least one CF slot. Due to the hybrid standards used by CF, you can also use a PCMCIA adapter to add additional CF storage to your device. For more information on using CF cards in your device see: CESDH0013 - Using a CF Storage Card For information on compatible CF Cards and other hardware devices for your Handheld PC please see the HPC:Factor Hardware Compatibility List. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||